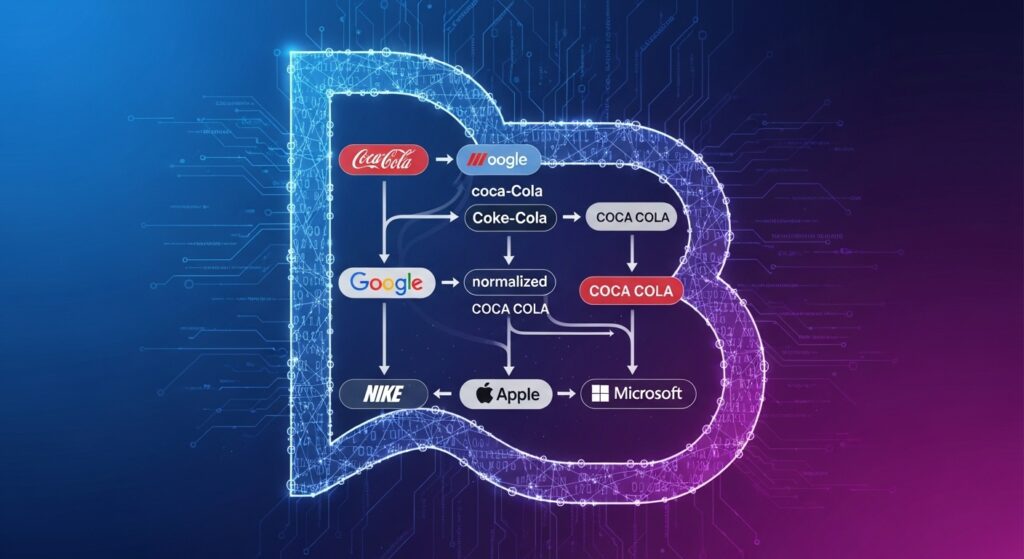
In today’s data-driven and omnichannel business environment, consistency is more than a branding ideal—it is a technical necessity. Companies collect, process, and analyze massive volumes of data from multiple sources, each using slightly different naming conventions. Without a structured way to standardize these variations, data quickly becomes fragmented and unreliable. This is where brand name normalization rules come into play.
These rules form the backbone of consistent brand representation across databases, analytics platforms, search engines, and customer-facing systems. While often operating behind the scenes, they directly influence data quality, reporting accuracy, and even customer trust. This article explores the concept in depth, explaining why it matters, how it works, and how organizations can implement it effectively.
Understanding the Concept of Brand Name Normalization
Brand names rarely appear in a single, perfectly formatted way. Variations emerge due to abbreviations, spelling differences, punctuation, localization, and user-generated input.
Why Brand Names Become Inconsistent
Inconsistencies arise for many reasons. Customers may type brand names differently, vendors may use internal abbreviations, and legacy systems may store outdated formats. Over time, these differences create multiple representations of what should be a single entity.
The Purpose of Normalization
Normalization aligns all these variations into one standardized format. This ensures that every reference to a brand points to the same recognized identity, regardless of how it was originally entered or sourced.
Brand name normalization rules Explained
Defining brand name normalization rules
Brand name normalization rules are structured guidelines used to transform different brand name variations into a single, consistent standard. These rules define how names are corrected, formatted, capitalized, abbreviated, or merged across systems.
Core Objectives of Normalization Rules
The primary goals include improving data accuracy, enabling reliable analytics, supporting automation, and maintaining brand integrity across platforms.
The Role of Normalization in Data Quality
Poor data quality is one of the most expensive and overlooked business problems. Brand inconsistency is a major contributor to this issue.
Eliminating Duplicate Records
When the same brand appears under multiple names, systems may treat them as separate entities. Normalization rules prevent duplication and reduce data clutter.
Improving Reporting Accuracy
Accurate reporting depends on consistent data inputs. Standardized brand names ensure metrics such as sales, engagement, and sentiment are calculated correctly.
Why Businesses Need Brand Name Normalization
Normalization is not just for large enterprises. Organizations of all sizes benefit from consistent brand data.
Supporting Business Intelligence
Dashboards, KPIs, and forecasting models rely on clean data. Inconsistent brand names distort insights and lead to poor decision-making.
Enhancing Customer Experience
Customers expect brands to appear consistently across touchpoints. Discrepancies can cause confusion and reduce trust.
Brand name normalization rules in Real-World Applications
E-commerce and Product Catalogs
Online marketplaces often aggregate products from multiple sellers. Normalization ensures that all listings for the same brand are grouped correctly.
Marketing and Advertising Platforms
Campaign performance analysis depends on accurate brand attribution. Normalized names ensure spending and results are correctly aligned.
Common Challenges in Brand Name Normalization
Despite its importance, normalization is not always straightforward.
Handling Abbreviations and Acronyms
Brands are frequently shortened in informal contexts. Determining which abbreviations should map to official names requires careful rule design.
Managing Regional Variations
Some brands use different naming conventions in different countries. Normalization rules must account for localization without losing global consistency.
Manual vs Automated Normalization Approaches
There are different ways to implement normalization, each with its own advantages.
Manual Rule Creation
Manual normalization involves defining rules based on known variations. While precise, it can be time-consuming and difficult to scale.
Automated and AI-Assisted Methods
Modern systems use machine learning to detect patterns and suggest normalization mappings, significantly reducing manual effort.
Building Effective Normalization Rules
Creating reliable rules requires both technical and business understanding.
Establishing a Canonical Brand List
A single source of truth for approved brand names is essential. This list acts as the foundation for all normalization efforts.
Defining Transformation Logic
Rules may include removing punctuation, standardizing capitalization, or replacing common misspellings with the correct form.
Maintaining Normalization Over Time
Normalization is not a one-time task. Brands evolve, merge, and rebrand.
Updating Rules for New Brands
As new brands enter the system, rules must be updated to ensure they are properly recognized and standardized.
Monitoring Rule Effectiveness
Regular audits help identify gaps or errors in normalization logic and ensure continued accuracy.
Impact on Search and Discoverability
Consistency plays a major role in how brands are indexed and discovered.
Improving Internal Search Results
Normalized brand names ensure users find all relevant results, regardless of how they search.
Supporting External SEO Efforts
Search engines favor consistency. Standardized brand references contribute to clearer brand signals across the web.
brand name normalization rules and Data Governance
Normalization is a key component of broader data governance strategies.
Aligning Teams and Systems
Clear rules ensure that marketing, sales, finance, and IT all work with the same brand definitions.
Reducing Compliance Risks
Accurate brand data supports regulatory reporting and reduces the risk of misrepresentation.
Measuring the Success of Normalization Efforts
To justify investment, organizations need measurable outcomes.
Key Performance Indicators
Metrics may include reduced duplicate records, improved reporting accuracy, and faster data processing times.
Long-Term Business Value
Over time, normalization contributes to better strategic planning, stronger brand equity, and operational efficiency.
The Future of Brand Normalization
As data ecosystems grow more complex, normalization will continue to evolve.
Integration with AI and NLP
Advanced systems will increasingly use natural language processing to understand brand context and intent.
Greater Emphasis on Real-Time Processing
Future normalization frameworks will operate in real time, ensuring consistency as data is generated.
Conclusion
In a world where data drives decisions, consistency is a competitive advantage. brand name normalization rules provide the structure needed to unify fragmented brand data, ensuring clarity, accuracy, and reliability across systems.
Though often invisible to end users, these rules play a critical role in analytics, customer experience, governance, and brand integrity. Organizations that invest in thoughtful normalization strategies position themselves to scale more effectively, gain deeper insights, and maintain a trustworthy digital identity in an increasingly complex landscape.